There are situations in real life when we need to do some specific task and based on some specific conditions, we decide what we should do next. Similarly, there comes a situation in programming where a specific task is to be performed if a specific condition is True. In such cases, conditional statements can be used. The following are the conditional statements provided by Python .
Let us go through all of them.
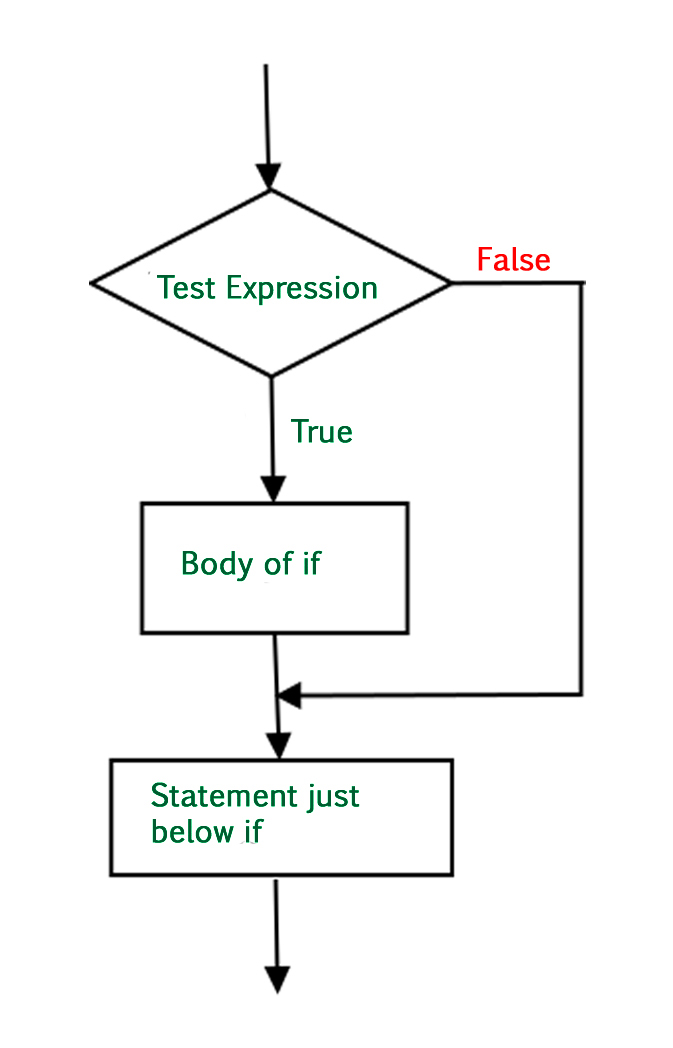
If the simple code of block is to be performed if the condition holds true then the if statement is used. Here the condition mentioned holds then the code of the block runs otherwise not.
Syntax : if condition:
# Statements to execute if
# condition is true
Below is the flowchart by which we can understand how to use if statement in Python:

In this example, an if statement checks if 10 is greater than 5. If true, it prints “10 greater than 5”; regardless, it then prints “Program ended” as the next statement, indicating the program flow.
10 greater than 5 Program ended
Indentation(White space) is used to delimit the block of code. As shown in the above example it is mandatory to use indentation in Python3 coding.
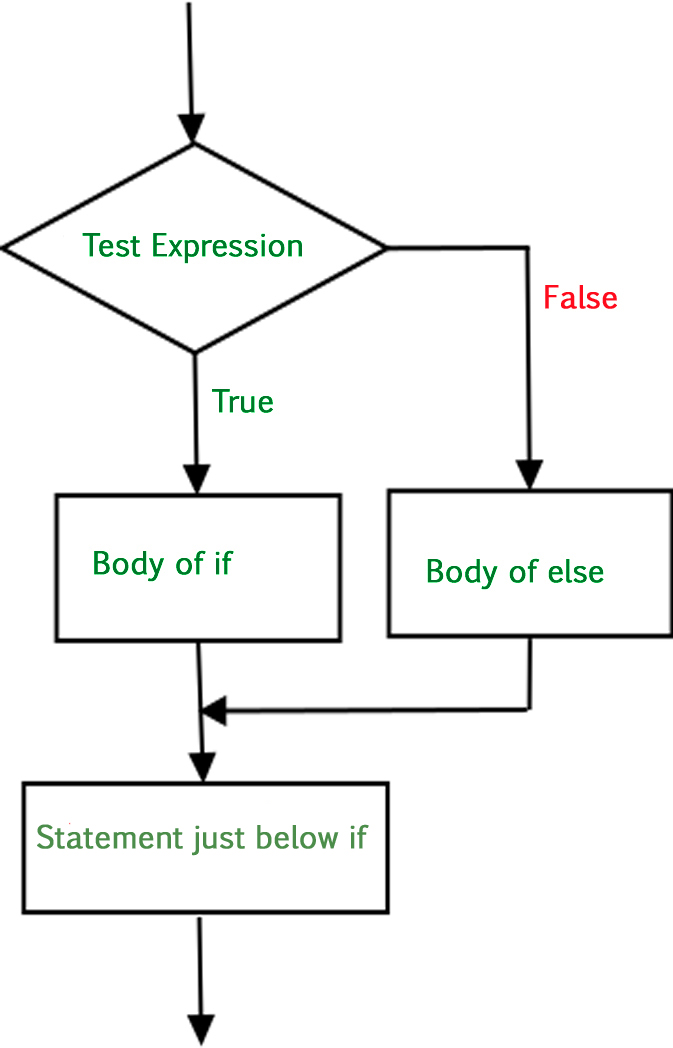
In conditional if Statement the additional block of code is merged as else statement which is performed when if condition is false.
Syntax : if (condition): # Executes this block if # condition is trueelse: # Executes this block if # condition is false
Below is the flowchart by which we can understand how to use if-else statement in Python:
In this example, the code assigns the value 3 to variable x and uses an if..else statement to check if x is equal to 4. If true, it prints “Yes”; otherwise, it prints “No,” demonstrating a conditional branching structure.
You can also chain if..else statement with more than one condition. In this example, the code uses a nested if..else chain to check the value of the variable letter . It prints a corresponding message based on whether letter is “B,” “C,” “A,” or none of the specified values, illustrating a hierarchical conditional structure.
letter is A
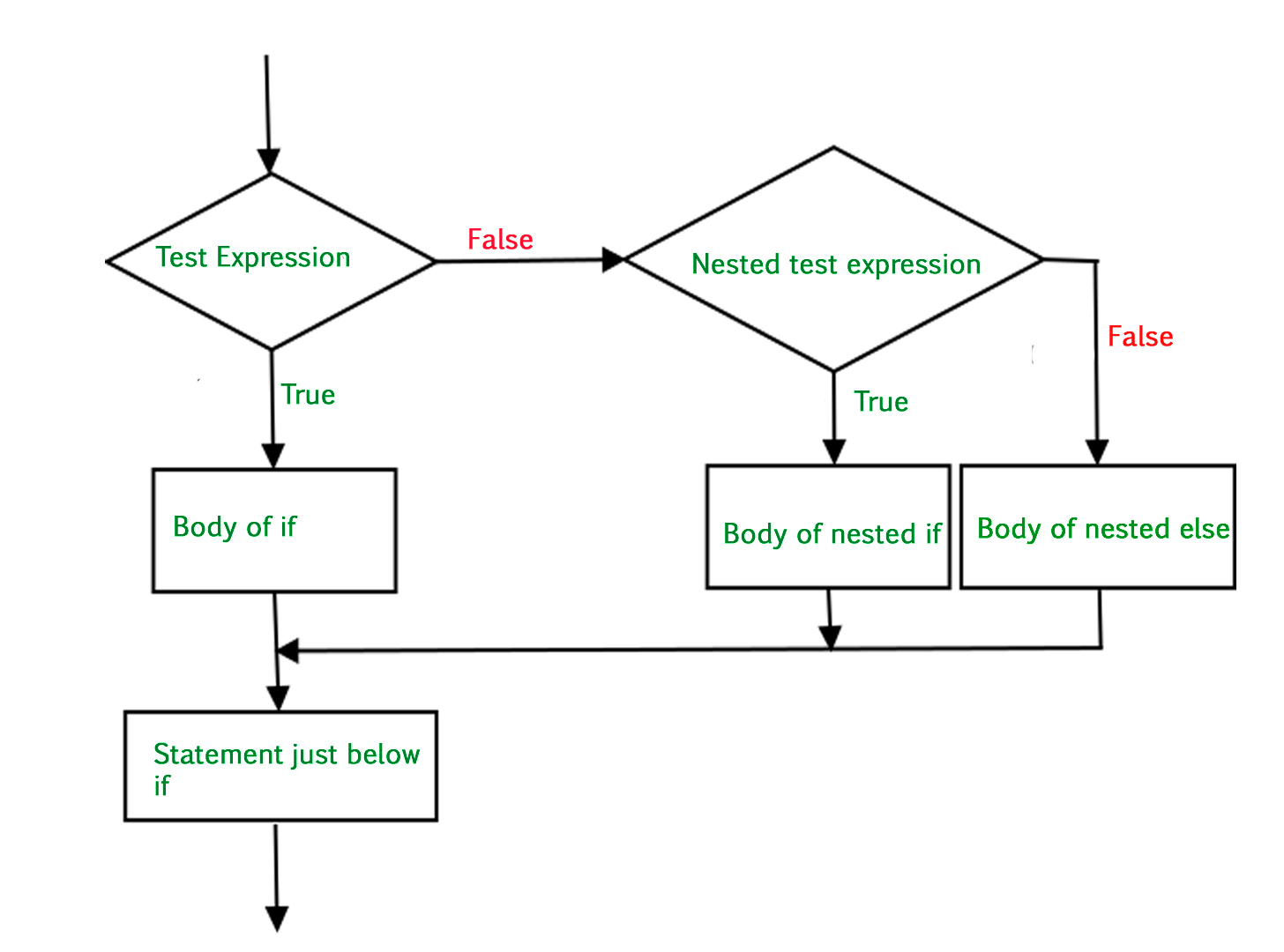
if statement can also be checked inside other if statement. This conditional statement is called a nested if statement. This means that inner if condition will be checked only if outer if condition is true and by this, we can see multiple conditions to be satisfied.
Syntax : if (condition1): # Executes when condition1 is true if (condition2): # Executes when condition2 is true # if Block is end here# if Block is end here
Below is the flowchart by which we can understand how to use nested if statement in Python:
In this example, the code uses a nested if statement to check if the variable num is greater than 5. If true, it further checks if num is less than or equal to 15, printing “Bigger than 5” and “Between 5 and 15” accordingly, showcasing a hierarchical condition for refined control flow.
Bigger than 5 Between 5 and 15
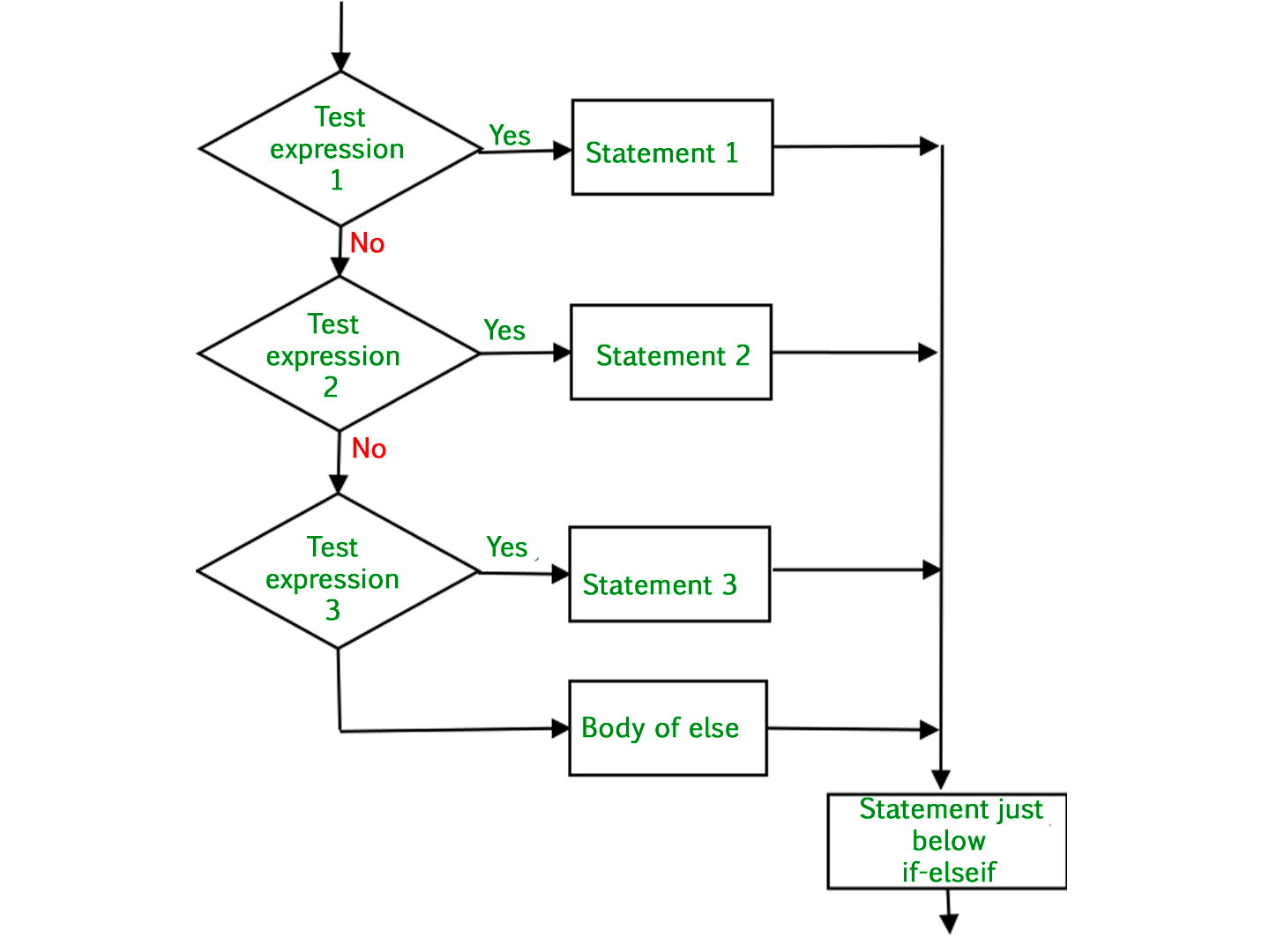
The if-elif statement is shortcut of if..else chain. While using if-elif statement at the end else block is added which is performed if none of the above if-elif statement is true.
Syntax : if (condition): statementelif (condition): statement..else: statement
Below is the flowchart by which we can understand how to use elif in Python:
In this example, the code uses an if-elif-else statement to evaluate the value of the variable letter . It prints a corresponding message based on whether letter is “B,” “C,” “A,” or none of the specified values, demonstrating a sequential evaluation of conditions for controlled branching.
letter is A
Yes, you can use elif within nested if statements in Python. This allows for more complex decision structures within a branch of another decision. For example:
pythonx = 10
y = 5
if x > 5:
if y > 5:
print("x and y are greater than 5")
elif y == 5:
print("x is greater than 5 and y is 5")
else:
print("x is greater than 5 and y is less than 5")
This structure provides conditional checks within another conditional check, enhancing the decision-making capabilities of your code.
Yes, you are allowed to nest if statements inside other if statements in Python. This is a common practice used to make more complex conditional logic possible. Nested if statements can be as deep as you need, although deep nesting can make your code harder to read and maintain.
Yes, you can use multiple if statements instead of elif , but the behavior of your code will change. elif allows for mutually exclusive conditions; only one branch can execute. With multiple if statements, each if condition is checked independently of others, so multiple branches might execute.
x = 10
y = 5
if x > 5:
if y > 5:
print("x and y are greater than 5")
elif y == 5:
print("x is greater than 5 and y is 5")
else:
print("x is greater than 5 and y is less than 5")
Using elif , the second condition would only be checked if the first condition failed.
Python does not explicitly limit the number of elif clauses you can have after an if statement. The practical limit is generally dictated by the readability and complexity of your code. Technically, you could have hundreds or even thousands, but this would be poor practice in terms of code clarity and maintainability. If you find yourself using many elif statements, consider refactoring your code, possibly using a different data structure like a dictionary to map conditions to functions or outcomes, or using a different logic flow altogether.