
12/07/201 Advice for parents section: reference to April 2021 NICE guidance stating that use of antimicrobial impregnated central catheters are not recommended.
This guideline is applicable to all neonatal staff caring for babies requiring Peripherally Inserted Central Catheters (PICC Lines). It is imperative that all practitioners inserting these lines should be aware of correct insertion techniques and that all staff involved in the care of these lines are aware of the hazards associated with their insertion and subsequent use.
It is mandatory that any practitioner wishing to learn to insert PICC lines have read this document before attempting to insert a PICC line for the first time.
Expand all Collapse all Use of PICC lines* Where possible veins suitable for PICC lines (e.g. saphenous vein) should not be used for peripheral cannulation and venesection in the first few days to leave them available for this purpose.
Choice of cathetersThe available neonatal PICC lines are listed below with the manufacturer’s product characteristics quoted.
Introducer Needle Gauge
20 G Microflash
Catheter Priming Volume
0.2 ml
(each lumen)
Max Flow rate
(at 1 Bar)
87 ml/h
(each lumen)
*NB - Premicaths were designed for babies Alternative introducer devices
Ref No
Size
Vygon Microflash
N.B. – Microflash cannulae may be available in some PICC sets but are available separately on the above code should an additional or alternative introducer cannula be required.
Vygon Microsite

The Vygon Microsite uses a Seldinger technique to insert any of the above PICC lines starting with a 24G needle or 24G IV cannula. Note that the PICC line is not included in this set
PICC line placement siteCommon sites of PICC line insertion
There are multiple potential sites for PICC line insertion.
The most commonly used are the antecubital and basilic veins in the upper limbs and the long saphenous veins in the lower limbs.
Axillary and scalp veins may also be used.
The operator should take time to identify the most suitable point for venous cannulation
A number of suitable veins lie in close proximity to arteries risking inadvertent cannulation of an artery. See later section – Specific risks of malposition
DocumentationDocumentation is essential when placing, manipulating or removing any invasive line.
The operator should record in the notes the following information:
 |  |
Insert the cannula into the chosen vein. A 24ga yellow cannula may be used if preferred
Insert the guidewire through the needle or cannula. Either end may be used. A mark on the wire indicates when the wire starts to enter the vein
Withdraw the needle / cannula ensuring that the wire remains in place
Insert the Microsite cannula over the wire. Use a little rotation of the cannula to ease the tip through the skin. Ensure the outer part of the cannula is well into the vein
Remove the inner part of the cannula and the guidewire
Pass the PICC line (Nutriline) through the Microsite catheter to the measured length
Withdraw the Microsite catheter until the tip is outside the skin and then split the catheter off the PICC line. Secure the PICC line
PICC line tip positionThe optimal position for the distal tip of a PICC line is in the SVC or IVC but clearly outside the cardiac silhouette.
It is not always possible to advance a PICC line to the predetermined position and it may be necessary to use a PICC line which lies within a large vein more peripheral than the optimal position however the operator must be aware of the increased risk of malposition under these circumstances. The use of a PICC line where the tip lies outwith the SVC/IVC must be sanctioned by a consultant and, where available, following radiological advice. It may be necessary to do additional imaging +/- the use of contrast media to provide further reassurance about the position of the line.
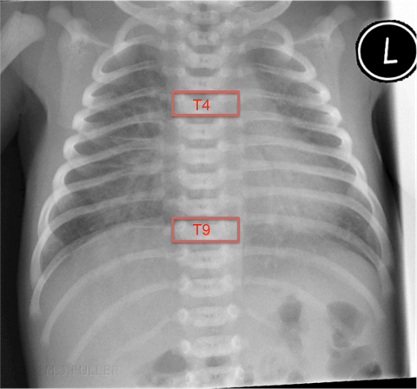
Fig.2 Neonatal CXR with maximal insertion landmarks
The following is a list of ‘red flags’ which raise the possibility of malposition
“Short” long line
Not infrequently, a PICC line cannot be advanced as far as planned during preparation for the procedure. In many cases these lines are within a large vein but short of the IVC/SVC. In a few cases the tip of the line may be embedded in the wall of the vessel or it may have entered a small tributary vessel. Such tributary vessels are commonest around the large joints such as the hip or shoulder. PICC lines in these locations are prone to thrombosis and extravasation and may cause local injury if this occurs.
It is sometimes necessary to use a PICC line which cannot be advanced into the SVC/IVC, but which sits instead in a large vein short of the preferred location. This is usually the case where no other suitable vessels are identified to place an alternative line. Extra care must be taken to ensure that the tip is within a large vein.
Lines in these positions should be replaced or removed as soon as practicable.
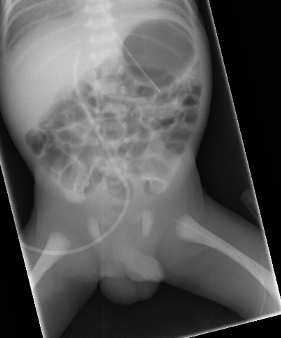
PICC line which has failed to advance beyond the hip joint
Inadvertent insertion into the lumbar vein
This complication is rare and predominantly affects PICC lines inserted into the left leg. Possible warning signs that the line has entered the lumbar vein may include some of the following:
If there are any concerns that this complication has occurred, a lateral x-ray may show the line deviating posteriorly. If possible, seek advice from radiology about further imaging.
Such lines must not be used and the catheter should be removed. These lumbar veins are small, and extravasation of the infusate into the spinal canal may readily occur. This may result in permanent neurological injury and seizures.
These two x-rays show PICC lines that have entered the left lumbar vein. In both cases the line has not crossed the midline and lie to the left of the spine.
Cardiac tamponade
This complication may occur if the tip of the PICC line lies within the heart. To avoid this complication the tip of all PICC lines must be seen clearly outside of the cardiac silhouette. See advice on imaging above. Cases have been recorded where the tip appears to have migrated after the initial X-ray. To guard against this, the tip of the line should be noted on any subsequent x-ray taken for other reasons. The following symptoms and signs may alert the clinician that tamponade has occurred
Cardiac tamponade can be easily diagnosed using an ultrasound scanner as there will be a large collection of fluid around the heart. See appendix for the procedure for aspiration of a cardiac tamponade.
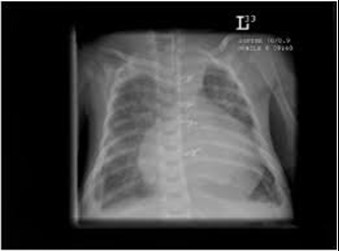 | 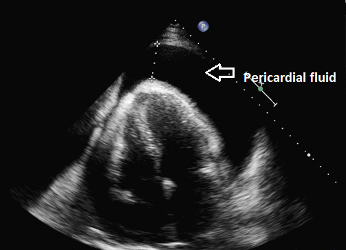 |
Inadvertent placement in an artery
There are a number of locations where an artery lies in close proximity to a vein which may be selected for PICC line insertion. All operators must be aware of the local anatomy.
The ankle
The saphenous vein runs anterior to the medial malleolus
The posterior tibial artery runs posteriorly
The elbow
The brachial artery lies between the basilic and cephalic veins
The scalp
The temporal artery lies just in front of the temporal vein
Possible warning signs suggesting inadvertent cannulation of an artery include some of the following:
If there are suspicions that an artery may have been cannulated, the line must not be used until correct placement has been confirmed. Opinion should be sought from the attending consultant. If the limb becomes ischaemic the line should be removed immediately.
Other hazardsPerforation of the microbore catheter tubing
The polyurethane tubing of a PICC line is very thin and the lines can burst if too much pressure is applied. To avoid this complication the following precautions should be taken:
Damage to the PICC line due to gate clamps
The gate clamp on the PICC line's extension tubing may cause a fracture of this tubing if used too close to the catheter hub, if left closed for extended periods or if repeatedly used on the same portion of the tubing.
Removal of a PICC line and the risk of the line snapping
A PICC line may become adherent to the tissues around the insertion site especially if it has been in situ for a prolonged period. If significant resistance is felt when removal is attempted then the operator should cease and seek senior advice as the line could snap leaving a portion within the vein, which may be very difficult to remove.
Breakage of Premicath lines
These catheters are more prone to breakage (snapping or bursting) than wider bore catheters. This is due to a number of factors including their very thin walls. Antiseptic solutions may weaken the catheter material and should not come into direct contact with the catheters. Ensure antiseptic solutions used to clean the skin are allowed to dry thoroughly before starting the catheter insertion. The catheters may be prone to fracture at the junction of the thin polyurethane section and the wider microbore tubing. This junction should be secured under the dressing to support this vulnerable area.
Bacterial / Fungal colonisation and sepsis
If bacteraemia or fungaemia occur whilst a PICC line is in situ the lines may easily become colonised. This can also occur if inadequate aseptic precautions are observed during insertion or when accessing the line when changing infusion fluids.
Such colonisation is very difficult to eradicate whilst the line remains in situ.
Failure to remove PICC lines in the face of bacterial or fungal sepsis is associated with failure of antimicrobial treatment and increased morbidity and mortality particularly with fungal sepsis.
If a PICC line is in situ when a neonate becomes septic then withdrawal of the line would be appropriate in most cases. If the line is vital because of very difficult vascular access, and where it is clear that long term central venous access will be required (e.g. babies with “intestinal failure”) the situation should be discussed with the NICU consultant as it may be more appropriate to initially treat the infection and conserve the line. Where the decision is made to retain the line for such reasons, this should be clearly documented. It is prudent to remove the line at the point of discontinuation of antimicrobial therapy as there may be a significant risk of recurrent infection.
All central lines should be inserted using full aseptic precautions. Each lumen should be capped with a needle-free connector. See separate advice about aseptic precautions to be taken when accessing central lines.
Advice for parentsAll vascular access devices have associated hazards. Before the insertion of a PICC line, the following information should be discussed with the parents before insertion.
(unless urgent vascular access is required when the parents are unavailable)
Placing PICC lines is a skilled procedure. All Medical staff or ANNPs placing these lines are required to be trained under the supervision of senior colleagues. In addition, they are required to have read this guideline to ensure they are familiar with the technique and the possible hazards.
Why we use PICC lines
Peripheral vascular catheters (PVCs) are useful for short term access to a baby’s veins, for the administration of fluids and medications. PVCs have significant limitations. Small peripheral veins thrombose readily. This requires replacement of the PVC and it may take some time before the affected vein recannalises allowing it to be used again. If vascular access is required on an ongoing basis we frequently run out of peripheral veins to use for PVC access. When the vein thromboses there may be an extravasation of the IV fluids or medications and this may cause a significant extravasation injury. This risk is increased where the osmolality of the fluid is high e.g. TPN, glucose (>10% solution) or if an infused medication is particularly irritant e.g. Bicarbonate, Calcium Chloride, Ganciclovir. Refer to the WoS guideline on extravasation injury for a full list of fluids for which there is an increased risk of such injury.
We recommend the placement of a central vein catheter when we are likely to run out of peripheral veins for PVC placement or where we need to infuse TPN or other irritant fluid. A UVC may be placed after birth but there are national recommendations that we limit the use of these lines to between 7 and 10 days.
Misplacement or Displacement:
The PICC line tip should come to rest in the Superior or Inferior Vena Cava (large veins which bring blood back to the heart from the body).
Lines may insert too far: Although we measure the baby to estimate the correct length for insertion, the line may be found to have reached the heart. If so the line must be withdrawn to the desired location and re x-rayed.
Lines which do not reached the planned position: Occasionally the line does not pass smoothly to reach the desired location and this may occur for a number of reasons.
The commonest reason is that the veins are simply too small and the line may not be able to advance as far as we would like. If the tip reaches a large vein but does not pass as far as the vena cava, the line may still be able to be used but it will not last as long as a line placed in the vena cava.
Less commonly the tip of the line may have become lodged in the wall of the vein or entered a smaller blood vessel which connects to the larger veins. If this is recognised then the line may be partially withdrawn and re x-rayed. If the line is not pulled back the vein may eventually rupture, allowing the parenteral nutrition fluid or medications to leak into the surrounding tissues. If this is not recognised the leaking fluid may cause injury to the surrounding tissues which may have serious consequences depending on exactly where the fluid leaks.
Medical staff are aware of instances where such a misplacement has not been recognised and our guideline now includes more detail of the warning signs that misplacement has occurred.
Lines which move after insertion: PICC line tips have been demonstrated to ‘migrate’ after insertion, i.e. the tip of the line is seen to have moved further into the baby on a later x-ray. All medical staff are reminded to check the line position on each x-ray taken whilst the line is in position. (We do not take regular x-rays specifically to look at the line as we must also limit the amount of radiation to which the babies are exposed.)
Damage to lines
Perforation: This may occur when fluid passes through the line under too high a pressure. We limit the pressure on the pumps and we advise medical staff flushing lines not to use small syringes as these exert the greatest pressure. Although perforation of the line does not usually cause injury directly, it does mean that the line will need to be replaced
Infection of the lines:
Any device which passes through the skin may become colonised with bacteria or fungi if it remains in position for long enough. Medical and nursing staff are all trained in hand hygiene and aseptic technique both during insertion and during later care of the line.
If the line does become colonised and the baby develops an infection it is usual practice to consider removing the line as this will speed the recovery from infection.
In some cases the line may be the only access we have to the baby’s veins and under these circumstances the medical staff may decide to leave the line in place and treat the infection through the line. The line can be removed when other vascular access is possible, or at the end of treatment.
N.B. NICE have recently recommended that there is no evidence to support the use of antimicrobial impregnated central catheters and that these catheters are not recommended (Neonatal infection: antibiotics for prevention and treatment NG195 April 2021)
Appendix: Emergency Management of Cardiac TamponadeCardiac tamponade is a rare complication of PICC line use in neonatal units. It is a medical emergency, with associated morbidity and mortality. Literature suggests an incidence of 0.76% to 3% in infants with PICC lines. Retrospective data from the UK estimate an incidence of 0.2%, with a mortality of 0.7 per 1000 neonates. Initial resuscitation should be methodical and follow recognised life support guidelines. Siting catheter tips outwith the cardiac border does not completely abolish the risk of pericardial effusion, or cardiac tamponade. 12
Pericardiocentesis should only be performed by skilled operators, under ultrasound guidance, unless a delay in treatment would be life threatening. If it is not possible to await ultrasound-guided drainage, emergency pericardiocentesis should be attempted by the most experienced neonatal practitioner available.
In subacute cases, where infusate pericardial effusion is suspected, there may be a role for aspirating the PICC line in-situ. This should be discussed with the Consultant on-call.
Clinical Signs:
Investigations:
Equipment:
Procedure:
Fig. 4 IV Cannula & 10ml syringe
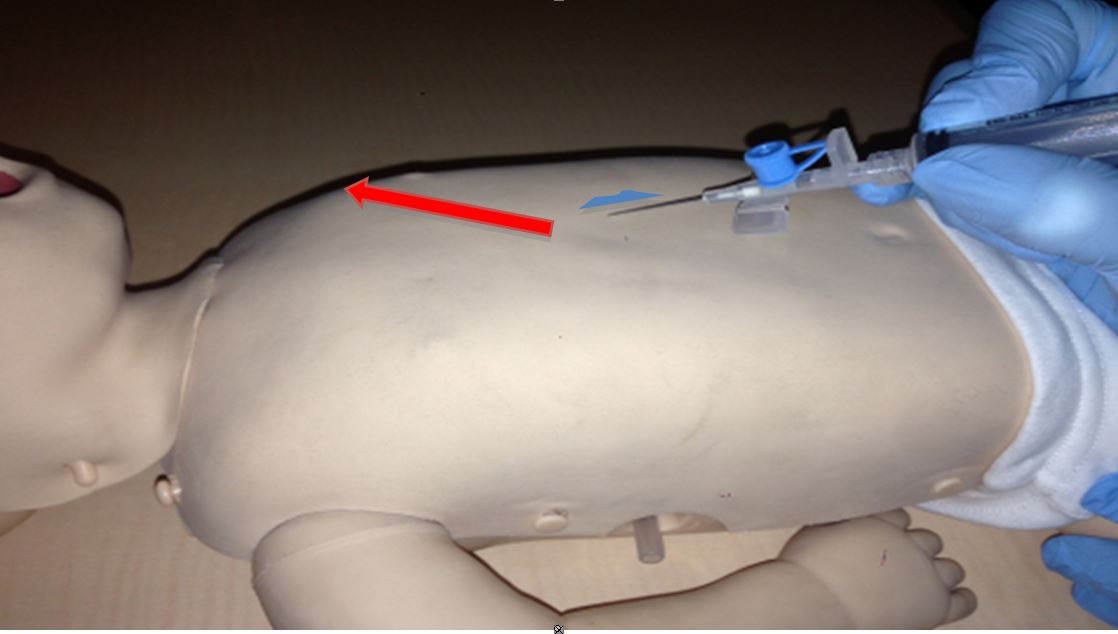
Fig.5 Approach for emergency pericardiocentesis
MHRA Device Alert - DA2001(04). The Use of Central Intravenous Access in Neonatal Parenteral Feeding
A Reece, T Ubhi, A R Craig and S J Newell. Positioning long lines: contrast versus plain radiography. Arch. Dis. Child. Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2001;84; F129-130.
Editorial InformationLast reviewed: 07 July 2021
Next review: 01 July 2024
Author(s): Dr A Powls – Consultant Neonatologist PRM
Co-Author(s): Other Professionals consulted: Dr Allan Jackson – Consultant Neonatologist PRM; Dr Joyce O’Shea – Consultant neonatologist RHC; Dr Ruth Allen – Consultant Radiologist RHC; Dr Jon Staines – Consultant Paediatrician Ayrshire
Approved By: West of Scotland Neonatology Managed Clinical Network